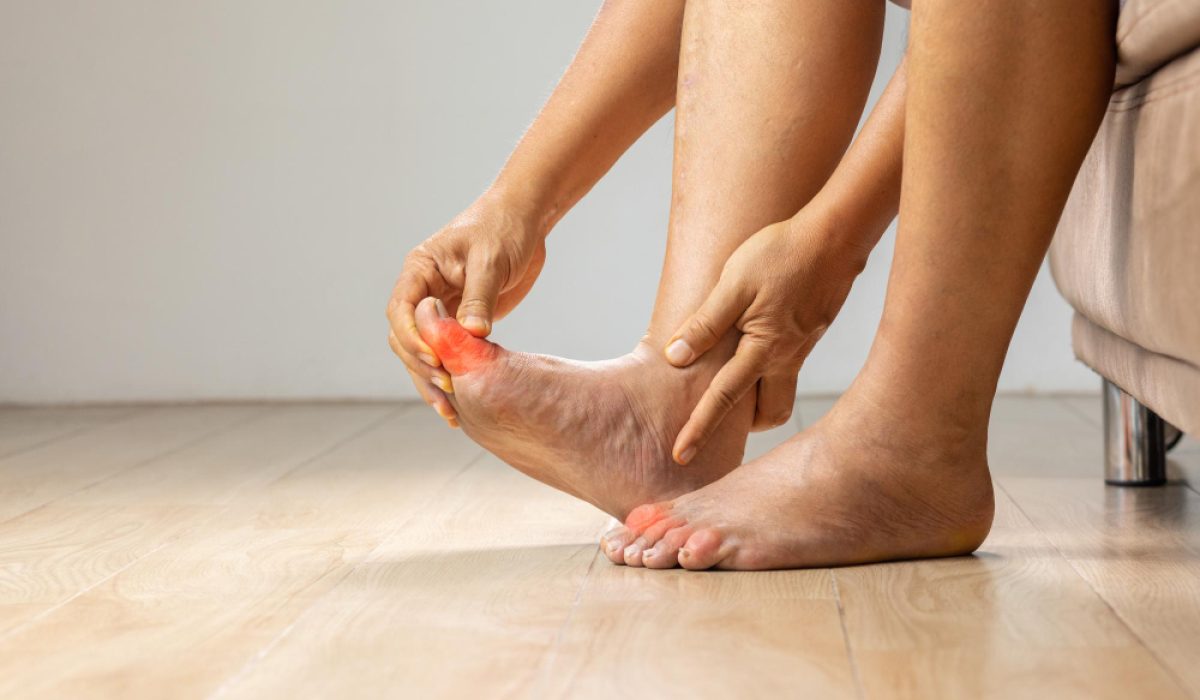
Gout is a type of arthritis that causes sudden joint pain, swelling, and redness. Often, it affects the big toe, but it can strike other joints too. Many people wonder about gout symptoms, gout causes, and how the gout diagnosis process works. In this blog, you will learn what gout is, why it happens, how it feels, and how doctors find out if you have it.
What Is Gout?
Gout is a painful joint condition. It happens when too much uric acid builds up in your blood. Uric acid is a waste product that forms when your body breaks down certain foods. Usually, your kidneys remove uric acid through urine. However, sometimes your body makes too much, or your kidneys cannot get rid of it fast enough. As a result, uric acid forms sharp crystals in your joints. These crystals cause swelling, pain, and redness. According to the CDC, gout is one of the most common types of arthritis in adults.
Causes of Gout
There are several reasons why gout may develop. Most often, it is linked to high levels of uric acid in the blood. But, other factors can also play a role. Here are some common causes and risk factors:
Because many things can cause gout, it is important to know your own risk factors. If you have several, you may want to talk to your doctor.
Symptoms of Gout
Gout symptoms often appear suddenly, sometimes at night. The pain can be very strong. However, not everyone has the same symptoms. Here are the most common signs:
Sometimes, gout can affect more than one joint. For example, it may also strike the ankles, knees, or fingers. If you notice these symptoms, it is wise to seek medical help. Early treatment can prevent more attacks and joint damage.
How Gout Is Diagnosed
Doctors use several steps to diagnose gout. First, they will ask about your symptoms and medical history. Next, they will examine your joints for swelling, redness, and tenderness. But, to confirm gout, they may need more tests. Here is how the gout diagnosis process usually works:
Because other conditions can look like gout, these tests help make sure you get the right diagnosis. According to the CDC and Mayo Clinic, early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent lasting joint problems.
In summary, gout is a common and painful joint condition. It is caused by high uric acid levels and can lead to sudden, severe pain. If you think you may have gout, do not wait. Consult a healthcare specialist for personalized advice on gout.